In recent years, the effects of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) on the immune system have received a considerable interest, not only to investigate possible negative health impact but also to explore the possibility to favorably modulate immune responses. To generate beneficial responses, the immune system should eradicate pathogens while “respecting” the organism and tolerating irrelevant antigens. According to the current view, damage-associated molecules released by infected or injured cells, or secreted by innate immune cells generate danger signals activating an immune response. These signals are also relevant to the subsequent activation of homeostatic mechanisms that control the immune response in pro- or anti-inflammatory reactions, a feature that allows modulation by therapeutic treatments. In the present review, we describe and discuss the effects of extremely low frequency (ELF)-EMF and pulsed EMF on cell signals and factors relevant to the activation of danger signals and innate immunity cells. By discussing the EMF modulating effects on cell functions, we envisage the use of EMF as a therapeutic agent to regulate immune responses associated with wound healing.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00085/full
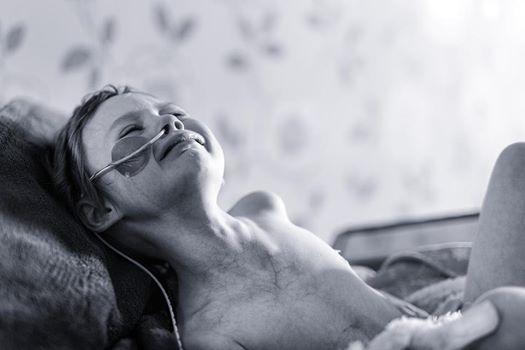
An attempt to wake up the medical community to accept research done in the last 100 years proving that electromagnetic energy can replace brutal chemotherapy. Photo taken by a professional photographer, of his own daughter being treated for Neuroblastoma. The power of the image encouraged Andy to share it with others in order to highlight the 'real' face of childhood cancer. She died. The average cost for such treatment is in the order of 500k+.
Thursday, May 31, 2018
The antitumor effect of static and extremely low frequency magnetic fields against nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma.
Certain magnetic fields (MF) have potential therapeutic antitumor effect whereas the underlying mechanism remains undefined. In this study, a well-characterized MF was applied to two common childhood malignancies, nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma. This MF has a time-averaged total intensity of 5.1 militesla (mT), and was generated as a superimposition of a static and an extremely low frequency (ELF) MF in 50 Hertz (Hz). In nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma cell lines including G401, CHLA255, and N2a, after MF exposure of 2 h per day, the cell viability decreased significantly after 2 days. After 3 days, inhibition rates of 17-22% were achieved in these cell lines. Furthermore, the inhibition rate was positively associated with exposure time. On the other hand, when using static MF only while maintaining the same time-averaged intensity of 5.1 mT, the inhibition rate was decreased. Thus, both time and combination of ELF field were positively associated with the inhibitory effect of this MF. Exposure to the field decreased cell proliferation and induced apoptosis. Combinational use of MF together with chemotherapeutics cisplatin (DDP) was performed in both in vitro and in vivo experiments. In cell lines, combinational treatment further increased the inhibition rate compared with single use of either DDP or MF. In G401 nephroblastoma tumor model in nude mice, combination of MF and DDP resulted in significant decrease of tumor mass, and the side effect was limited in mild liver injury. MF exposure by itself did not hamper liver or kidney functions. In summary, the antitumor effect of an established MF against neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma is reported, and this field has the potential to be used in combination with DDP to achieve increased efficacy and reduce side effects in these two childhood malignancies.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bem.22124
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bem.22124
Tuesday, May 29, 2018
Bio-soliton model that predicts non-thermal electromagnetic frequency bands, that either stabilize or destabilize living cells
Solitons, as self-reinforcing solitary waves, interact with complex biological phenomena such as cellular self-organization. A soliton model is able to describe a spectrum of electromagnetism modalities that can be applied to understand the physical principles of biological effects in living cells, as caused by endogenous and exogenous electromagnetic fields and is compatible with quantum coherence. A bio-soliton model is proposed, that enables to predict which eigen-frequencies of non-thermal electromagnetic waves are life-sustaining and which are, in contrast, detrimental for living cells. The particular effects are exerted by a range of electromagnetic wave eigen-frequencies of one-tenth of a Hertz till Peta Hertz that show a pattern of 12 bands, and can be positioned on an acoustic reference frequency scale. The model was substantiated by a meta-analysis of 240 published articles of biological electromagnetic experiments, in which a spectrum of non-thermal electromagnetic waves were exposed to living cells and intact organisms. These data support the concept of coherent quantized electromagnetic states in living organisms and the theories of Fröhlich, Davydov and Pang. It is envisioned that a rational control of shape by soliton-waves and related to a morphogenetic field and parametric resonance provides positional information and cues to regulate organism-wide systems properties like anatomy, control of reproduction and repair.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321268842_Bio-soliton_model_that_predicts_non-thermal_electromagnetic_frequency_bands_that_either_stabilize_or_destabilize_living_cells
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321268842_Bio-soliton_model_that_predicts_non-thermal_electromagnetic_frequency_bands_that_either_stabilize_or_destabilize_living_cells
Thursday, May 24, 2018
Electromagnetic Medicine Non-Inductive Non-Thermal Modalities
The area of electromagnetic medicine (EM) encompasses the applications of electricity and magnetism to medical practice. Although this includes both diagnostic and therapeutic applications, the medical community is far more familiar with the former, notably with techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electromyography (EMG), electroencephalography (EEG), electrocardiography (EKG), and magnetocardiography (MKG). There are historical reasons for the medical unfamiliarity (even antipathy) with electromagnetically-based therapies. One has only to look at the beginnings of modern medicine in the United States, specifically the 1910 Flexner report 1,2 that provided the basis for medical education today. Prior to this report there was widespread use of electromagnetic techniques in medicine, often little more than late 19th century versions of snake-oil cures. In great measure the present aversion to electromagnetic therapies built into modern medicine is a direct result of Victorian age quackery. Another reason for this antipathy, apart from the constraint on the teaching curriculum, has been the extraordinary success of, first, the germ theories of Pasteur and Koch, and, second, the development of molecular biology following the work of Watson and Crick. These have engendered a sense of completeness, a feeling that there is no place for alternate, radically new approaches to the way that illness is treated. Even when electromagnetically-based therapies have proven beneficial, they have been usually ignored. There is little impetus to replace the existing approach, since it is firmly believed that nothing is more fundamental than the existing paradigm, that questions of wellness and illness are ultimately biochemical in nature. The divisions in electromagnetic medicine are outlined in Fig. 1. Beyond the separation into diagnostic and therapeutic applications another distinction is made for applications of weak-field ELF magnetic in the treatment of illness. The description non-inductive non-thermal helps emphasize that the effects obtained by applying low intensity low-frequency electromagnetic fields to biological systems are not the result of either inductive emf generation or the delivery of thermal energies through Joule heating. By contrast, a number of clinical devices that make use of Faraday induction or Joule heating are recognized by the medical community not only because 3 they are effective, but also because the applied voltages, currents or heat are fully consistent with what is expected biochemically. In sharp contrast, the non-inductive non-thermal category includes clinical applications where this is not true, that is, where the electromagnetic variables that are part of the therapy fall outside those permitted by the current medical paradigm.
http://bioinitiative.org/report/wp-content/uploads/pdfs/sec17_2012_Electromagnetic_Medicine_non_thermal_modalities.pdf
http://bioinitiative.org/report/wp-content/uploads/pdfs/sec17_2012_Electromagnetic_Medicine_non_thermal_modalities.pdf
Tuesday, May 22, 2018
Electromagnetic frequencies of living cells and bio-molecules
In 1905 Einstein proposed the idea that electromagnetic radiation is quantized and appears only in defined energy packets. The energy of a photon for a given type of radiation can be computed using the frequency relation published in 1900 by Planck.
It is proposed in the present paper that the energy distribution of these packets is according to a Pythagorean distribution of frequencies.
Evidence for this hypothesis has been found by a meta-analyses of 500 biomedical papers related to electromagnetic frequencies of living cells and bio-molecules, in addition to an analyses of 60 papers in physics that deal with the influence of electromagnetic frequencies on the promotion of entangled states in Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen-experiments, as well as a study on measurements of the masses of 37 different elementary particles.
It turns out that Einstein was right, and that electromagnetic radiation is quantized according to a precise distribution of defined energy packets.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325013224_Evidence_for_a_Guiding_Coherence_Principle_in_Quantum_Physics
It is proposed in the present paper that the energy distribution of these packets is according to a Pythagorean distribution of frequencies.
Evidence for this hypothesis has been found by a meta-analyses of 500 biomedical papers related to electromagnetic frequencies of living cells and bio-molecules, in addition to an analyses of 60 papers in physics that deal with the influence of electromagnetic frequencies on the promotion of entangled states in Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen-experiments, as well as a study on measurements of the masses of 37 different elementary particles.
It turns out that Einstein was right, and that electromagnetic radiation is quantized according to a precise distribution of defined energy packets.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325013224_Evidence_for_a_Guiding_Coherence_Principle_in_Quantum_Physics
Friday, May 18, 2018
Cellular ATP levels are affected by moderate and strong static magnetic fields
Mitochondrion is the major cellular energy producing organelle that is at the boundary between chemical reactions and physical processes.
Although mitochondria have been shown to be affected by physical methods such as nonthermal plasma, whether static magnetic field (SMF) could also affect them is still unclear.
Here we used rat adrenal PC12 cells to compare SMFs of different intensities for their effects on ATP (adenosine‐5′‐triphosphate), the major energy source produced by mitochondria, which is essential for various cellular processes.
Our results show that although 0.26 or 0.50 T SMFs did not affect ATP, 1 T and 9 T SMFs affected ATP level differently and time‐dependently.
Moreover, SMF‐induced ATP level fluctuations are correlated with mitochondrial membrane potential changes.
Our study provides insights not only into understanding various cellular effects of SMFs, but also the potential clinical applications of SMFs.
Antitumor effect of static magnetic field against neuroblastoma
Certain magnetic fields (MF) have potential therapeutic antitumor effect whereas the underlying mechanism remains undefined.
In this study, a well-characterized MF was applied to two common childhood malignancies, nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma.
This MF has a time-averaged total intensity of 5.1 militesla (mT), and was generated as a superimposition of a static and an extremely low frequency (ELF) MF in 50 Hertz (Hz).
In nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma cell lines including G401, CHLA255, and N2a, after MF exposure of 2 h per day, the cell viability decreased significantly after 2 days.
After 3 days, inhibition rates of 17-22% were achieved in these cell lines.
Furthermore, the inhibition rate was positively associated with exposure time.
On the other hand, when using static MF only while maintaining the same time-averaged intensity of 5.1 mT, the inhibition rate was decreased.
Thus, both time and combination of ELF field were positively associated with the inhibitory effect of this MF. Exposure to the field decreased cell proliferation and induced apoptosis.
Combinational use of MF together with chemotherapeutics cisplatin (DDP) was performed in both in vitro and in vivo experiments.
In cell lines, combinational treatment further increased the inhibition rate compared with single use of either DDP or MF.
In G401 nephroblastoma tumor model in nude mice, combination of MF and DDP resulted in significant decrease of tumor mass, and the side effect was limited in mild liver injury.
MF exposure by itself did not hamper liver or kidney functions. In summary, the antitumor effect of an established MF against neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma is reported, and this field has the potential to be used in combination with DDP to achieve increased efficacy and reduce side effects in these two childhood malignancies.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29719057
In this study, a well-characterized MF was applied to two common childhood malignancies, nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma.
This MF has a time-averaged total intensity of 5.1 militesla (mT), and was generated as a superimposition of a static and an extremely low frequency (ELF) MF in 50 Hertz (Hz).
In nephroblastoma and neuroblastoma cell lines including G401, CHLA255, and N2a, after MF exposure of 2 h per day, the cell viability decreased significantly after 2 days.
After 3 days, inhibition rates of 17-22% were achieved in these cell lines.
Furthermore, the inhibition rate was positively associated with exposure time.
On the other hand, when using static MF only while maintaining the same time-averaged intensity of 5.1 mT, the inhibition rate was decreased.
Thus, both time and combination of ELF field were positively associated with the inhibitory effect of this MF. Exposure to the field decreased cell proliferation and induced apoptosis.
Combinational use of MF together with chemotherapeutics cisplatin (DDP) was performed in both in vitro and in vivo experiments.
In cell lines, combinational treatment further increased the inhibition rate compared with single use of either DDP or MF.
In G401 nephroblastoma tumor model in nude mice, combination of MF and DDP resulted in significant decrease of tumor mass, and the side effect was limited in mild liver injury.
MF exposure by itself did not hamper liver or kidney functions. In summary, the antitumor effect of an established MF against neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma is reported, and this field has the potential to be used in combination with DDP to achieve increased efficacy and reduce side effects in these two childhood malignancies.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29719057
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)